Swiss-based corporate think-tank, World Economic Forum (WEF), has released a new report on fintechs in which the notorious organization explores how disruptive innovations are transforming the financial services industry.
The fintech industry, which attracted some US$12.2 billion in global investments last year, is continuously pressuring banks and financial institutions to innovate as new entrants lay claim to more and more of the US$6.6 trillion on revenues at stake in global retail financial services.
„Innovation will shape customer behaviors, business models and the long-term structure of the financial services industry,“ argues Chris Harvey, Global Leader, Financial Services, at Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited.
„Banks and insurance firms are already starting to see the effect of disruptors, and we believe much more is to come.“
Released on June 30, the 178-page document resulted from over 15 months of interviews and workshops with executives from financial institutions, including Deutsche Bank, Morgan Stanley, HSBC, UBS and Santander, as well as prominent fintech startups, such as Lending Club, Prosper, TransferWise and Square.
In order to understand how these industry disruptors can potentially
transform business models in financial services, we have summarized the six key research findings from the WEF’s „Future of Financial Services“ report.
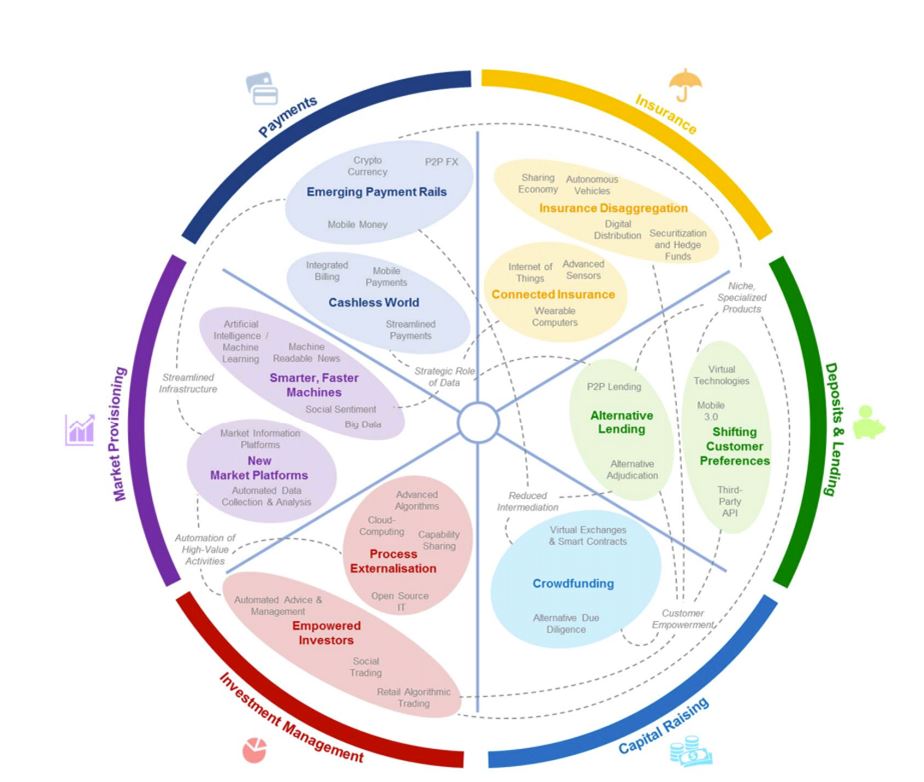
The six „innovation clusters“ – „The Future of Financial Services“ report, June 2015
1)Streamlined Infrastructure
Emerging platforms and decentralized technologies provide new ways to aggregate and analyze information, improving connectivity and reducing the marginal costs of accessing information and participating in financial activities.
Innovative payment systems create new consumer functionalities that will ultimately result in meaningful changes in consumer behavior. These disruptors leverage mobile and connectivity to make payments simpler, while creating competitive pressure for the value transfer rails to become faster, cheaper and borderless.
2)Automation of High-Value Activities
Many emerging innovations leverage advanced algorithms and computing power to automate activities that were once highly manual. These technologies allow them to offer cheaper, faster, and more scalable alternative products and services.
Wealth management disruptors provide low-cost, personalized and sophisticated alternatives to traditional wealth manager to a broader customer base. They offer high-value advisory services and money management at low costs based on automated analysis.
3)Reduced Intermediation
Emerging innovations are streamlining or eliminating traditional institutions’ role as intermediaries, and offering lower prices and / or higher returns to customers.
Decentralized and non-traditional payment schemes such as bitcoin, allow a global settlement infrastructure and challenge the role of traditional intermediaries as a trusted party.
Alternative models of lending (P2P) change the market dynamics of traditional lenders. New market entrants will make meeting customer demands more important, creating an imperative for banks to reconsider their roles.
4)The Strategic Role of Data
Emerging innovations allow financial institutions to access new data sets, such as social data, that enable new ways of understanding customers and markets.
Ubiquity of connected devices will enable insurers to highly personalize insurance and proactively manage clients‘ risks. Key disruptive trends include smarter and cheaper sensors, wearables, the „Internet-of-Things“ and standardized platforms.
With greater adoption of electronic payments, more data will be accumulated from payment transactions, allowing financial institutions, services providers and merchants to gain a greater understanding of customers and businesses.
As the popularity of high frequency trading declines, the focus of algorithmic trading may shift to smarter, faster response to real-life events. Key disruptive trends include the use of machine accessible data, artificial intelligence, machine learning and Big Data.
5)Niche, Specialized Products
New entrants with deep specializations are creating highly targeted products and services, increasing competition in these areas and creating pressure for the traditional end-to-end financial services model to unbundle.
Unbundling of a Bank – CB Insight
Alternative providers of niche financial services continue to mature and become reliable alternatives to offerings of traditional institutions.
These network of non-traditional niche providers collectively meet customers’ banking needs and compete with traditional full service banks. They also provide the ability to seamlessly mix and match niche providers that fit the clients‘ needs in a fashion not possible within today’s full service financial institutions.
6)Customer Empowerment
Emerging innovations give customers access to previously restricted assets and services, more visibility into products, and control over choices, as well as the tools to become “prosumers”.
Wealth management disruptors improve the financial literacy of customers by readily providing analysis of their financial position and empowering them with tools to easily create and execute investment strategies.
Crowdfunding platforms are widening access to capital raising activities, making the overall ecosystem richer. Alternative funding platforms enable the crowd to play a bigger role in providing capital to investment opportunities, empowering angel investors.
The full report can be found at: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_The_future__of_financial_services.pdf





Schreibe einen Kommentar